Do the thermosensitive products in the Biochemistry range remain functional in the event of temperature variations during transportation?
Yes. Although transportation should preferably take place between 2-8 °C, the thermosensitive products in the Biochemistry range maintain their functionality in the event of occasional temperature variations during transportation.
Most reagents remain stable for up to 7 days at temperatures of up to 37 °C, with the exception of the Urea, Amylase, Glucose and Gamma GT reagents, which tolerate temperature variations of up to 37 °C for a maximum of 48 hours.
Upon receipt, the products must be immediately stored under refrigeration at 2-8 °C to ensure their stability throughout use.
How stable are bireagent reagents when the working reagent is prepared?
The stability of the working reagent may vary according to the product, as long as it is kept at 2-8°, protected from light and with the bottle tightly closed.
- CKNAC: 15 days
- CKMB: 20 days
- Alkaline phosphatase: 60 days
- GT range: 21 days
- Lactate dehydrogenase: 60 days
Is it possible to use bireagent reagents in monoreagent form? What are they?
Yes. The CKNAC, CKMB, Alkaline Phosphatase, Gamma GT and Lactate Dehydrogenase reagents are available in bireagent form, but can be prepared for use in monoreagent form, in a 4:1 ratio (four parts of reagent 1 to one part of reagent 2).
The use of the single-reagent form optimizes the laboratory routine, as it allows the use of only one position on the equipment's carousel, reduces the number of pipetting operations, contributing to greater agility in the routine, as well as reducing the volume of GAP, providing a better cost-benefit ratio.
Are there any special recommendations for storing reagents in the fridge?
Reagents that require storage between 2-8°C should be kept under constant refrigeration, but some additional precautions are important to preserve their stability and performance.
We recommend the following good practices:
- Store the bottle away from fans or direct cold air vents;
- Avoid areas of the fridge where there is a risk of localized freezing;
- Before use, allow the reagent to reach room temperature and gently mix the contents.
Some reagents, such as Creatinine, are more sensitive to exposure to extreme cold air and have a higher risk of crystal formation. For this reason, careful storage in the fridge is essential to maintain the quality of the product.
What parameters can be measured in normal and pathological control?
The following parameters can be measured as controls: Uric acid, Albumin, AST/TGO, ALT/TGP, Amylase, Direct bilirubin, Total bilirubin, Calcium, Chlorides, Cholesterol, Creatinine, CPK, Alkaline phosphatase, Gamma GT, Iron, Phosphorus, Glucose oxidase, HDL cholesterol, Lactate dehydrogenase, Lactate, Lipase, Magnesium, Total protein, Triglycerides, Urea, Na+, K+ and Cl-.
What are the advantages of calibrating biochemical reagents compared to using a fixed factor?
Calibration makes it possible to adjust biochemical reagents according to the specific characteristics of each batch of reagent, resulting in more accurate and reliable analyses. In addition, by performing calibration, it is possible to identify and correct any systematic errors that may be present in the analyzer used.
How often should the kits be calibrated?
The kits should be calibrated whenever there is a batch change or if the controls do not perform well in the dosage results.
How can we dose samples that exceed the linearity limit of a kit?
If a sample exceeds the linearity limit of a kit, to enable accurate dosing, it must be diluted with a suitable diluent, such as saline or water, in the appropriate proportion. Dilution will reduce the concentration of the sample to a level within the kit's linear range, enabling accurate dosing. Make sure you choose a compatible diluent and consider the dilution factor when interpreting the results.
What does gap volume mean in the biochemical analyzer and what impact does this volume have on the kit's yield?
Analyzers usually consume additional volumes of reagent with each pipetting (for safety reasons in the event of aspiration of bubbles or instabilities in the pipetting modules). This safety volume is known as the "GAP volume". Due to this additional volume, the theoretical calculation (kit volume / volume per test) made to determine how many tests the kit is capable of performing will not be entirely faithful to the number of tests performed in practice.
How stable are the controls and multi-parameter calibrators on the Biochemistry line?
Unopened products are stable until the expiration date stated on the label. After reconstitution, they are stable for 7 days if stored between 2 - 8°C in a well-sealed vial and protected from light, except for the Direct Bilirubin, Total Bilirubin and Alkaline Phosphatase analytes which are stable for 2 days if stored between 2 - 8°C. All analytes, with the exception of bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase, are stable for 28 days when stored at -20°C, in an airtight container and protected from light. We recommend separating the calibrator and controls into aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Can the Chlorine kit be used for CSF dosages?
Yes, as long as the sensitivity and linearity limits of the test are complied with.
What is the procedure for measuring and calculating the concentration of Creatinine in urine?
To measure Creatinine in urine, it is not necessary to pre-treat the sample, just dilute it in a ratio of 1:25. In a simple urine sample, multiply the result found on the equipment by the dilution factor (x25). In the case of a 24-hour urine sample, the result provided by the equipment must be converted from mg/dL to g/L, multiplied by the dilution factor (x25) and multiplied by the urinary volume (L), which is the volume of urine collected in 24 hours.
Calculation: Creat. Sample (g/L) x dilution factor x Volume (L)
Which Ebram products can be used for urinary dosages?
Uric Acid, Amylase, Creatinine, Calcium, Chlorides, Phosphorus, Glucose, Magnesium, Urea and Proteinuria.
How do you calibrate biochemistry analytes that don't have a standard included in the kits?
Ebram sells a multi-parameter calibrator, called Quimicalib - Calibrator, which can be used for most biochemical tests, except for the HDL Cholesterol, Chloride and Proteinuria kits which have standards included in all presentations, and for the CKMB and Cholinesterase kit which use a fixed factor.
What is the main difference between the general and bulk biochemistry kits?
The general line kits have a reduced volume of reagent, perfect for smaller routines, and come with a standard solution (except enzymes) which is used for calibrating assays and performing manual techniques. The bulk line kits, which do not include standard solutions, have a larger volume of reagent, a lower cost per ml and the same quality.
What are the main features of Ebram's Biochemistry program?
We have different packaging to meet the needs of laboratories of all sizes, liquid and ready-to-use reagents with advanced stabilization technology and high linearity. Most of our products are mono-reagents, i.e. a single reagent that does not require the preparation of the working reagent.
Due to the high enzyme concentration, the volume of reagent per test is reduced, saving money, and its ions are prepared in such a way that they are less affected by external interferents and contaminants (drag-free).
Is it possible to put the sample tube directly into the EBCOAG Auto analyzer? Does the tube need to be open?
Yes, you can use the collection tube directly in the analyzer, as long as you remove the cap.
What are the precautions when using coagulation reagents?
It is important to homogenize the reagents before using them, especially the TP reagent, which tends to sediment due to its composition.
Do the EBCOAG Auto and EBCOAG 4.0 analyzers use magnetic beads?
No, the EBCOAG Auto and EBCOAG 4.0 analyzers do not use magnetic beads, as their methodology is based on optical technology. This methodology allows the precise detection of clot formation by means of the variation in the intensity of the light transmitted during the reaction, as well as being more modern, providing better reproducibility of results.
What is TP's ISI?
TP's ISI is 1.16.
How stable is the control after reconstitution?
The controls are lyophilized and have a stability of 6 hours after reconstitution.
How stable are the TP, TTPa, TT and FIB reagents once opened?
The reagents are stable for 14 days.
Which cleaning solution is used in EBCOAG 4.0?
For EBCOAG 4.0, it is recommended to use the cuvette washing solution - EBCOAG, code 752, which is indicated for manual cleaning of the coagulation cuvettes.
What cleaning solution is used in EBCOAG Auto?
EBCOAG Auto uses three solutions:
- Code: 750 - Solution for probe - EBCOAG (needle tip cleaning),
- Code: 751 - Washing solution - EBCOAG (internal analyzer cleaning),
- Code: 752 - Vial washing solution - EBCOAG (for manual cleaning of coagulation vials).
What is the minimum volume required for each reaction in the EBCOAG Auto and EBCOAG 4.0 analyzers?
- EBCOAG Auto (minimum reaction volume 150µL):
| TP | 100µL of TP reagent 50µL of sample |
|---|---|
| TTPa | 50µL of TTPa reagent 50µL Calcium reagent 50µL of sample |
| TT | 75µL of TT reagent 75µL of sample |
| GNH | 50µL of FIB reagent 100µL of sample |
- EBCOAG 4.0 (minimum reaction volume 300µL):
| TP | 200µL of TP reagent 100µL of sample |
|---|---|
| TTPa | 100µL of TTPa reagent 100µL of Calcium reagent 100µL of sample |
| TT | 150µL of TT reagent 150µL of sample |
| GNH | 200µL of FIB reagent 100µL of sample |
How does the cuvette exchange process work on the EBCOAG Auto analyzer?
Changing the cuvettes in EBCOAG Auto is done manually, simply and guided by the system itself. The analyzer's software informs you on the screen when the replacement is necessary, ensuring convenience and control during use.
Are the cuvettes of the EBCOAG Auto and EBCOAG 4.0 analyzers washable?
Yes, the cuvettes are reusable and washable. Ebram offers a specific cleaning solution (code 752) to ensure optimum performance.
How stable are Ebram's hematological controls?
Once opened, Ebracontrol 3 Parts will remain stable for 21 days, provided it is stored with the lid properly closed and kept at a temperature of 2-8°C. As for Ebracontrol 5 Parts and Ebracontrol 5 Parts (ABT), their stability is 8 days, provided they are stored with the lids properly closed and kept in a temperature range of 2-8°C.
Can Ebram hematology controls be used on equipment that is not marketed by Ebram?
Yes. Ebram has 3-part and 5-part controls. The 3-part control is compatible with the following Beckman Coulter equipment: models ST, STKR, STKS, MAXM, MD 8, MD 16, MD II, ACT 8, ACT 10 and ACT Diff, Abbott CD equipment: models 1400, 1600, 1700 and 1800 and also Micros 45, Micros 60, SDH 20, Mindray 2300, 2800, 3000 and 3200. The 5-part control is compatible with DH-53, DH-71, DF-50, DF-51, DF-52, DF-53, UN-71, UN-73, UN-76 and DH-73 devices. We also offer another presentation of the 5-part control, compatible with Cell Dyn 3500 and Cell Dyn 3700 units.
When changing hematology reagents for the Ebram line, is it possible to use another brand's diluent with the Ebram lysate or vice versa?
Ebram does not recommend mixing reagents from other brands with Ebram reagents. In order to guarantee the quality of the results, the customer must use the same brand of reagent (diluent+lysant+detergent) in the hematology counter.
Do the products in the Immunohematology line remain functional in the event of temperature variations during transportation?
Yes. Although transportation should preferably take place between 2-8 °C, the products in the Immunohematology line maintain their functionality in the event of occasional temperature variations during transportation.
The reagents remain stable for up to 7 days at temperatures up to 37 °C.
Upon receipt, the products must be immediately stored under refrigeration at 2-8 °C to ensure their stability throughout use.
How do you prepare a suspension of red blood cells at 3 and 5% for immunohematology tests?
To prepare a RBC suspension at 3% or 5%, follow the procedure below:
1. wash the red blood cells 3 times with 0.85% saline solution;
2. Using a pipette, add 500µL of red blood cells to a tube;
3. Add 4mL of 0.85% saline solution to the same tube;
4. Centrifuge for 1 minute at 3400 RPM;
5. After centrifugation, carefully decant the supernatant, without discarding the red blood cells, and repeat the washing procedure twice more;
6. Prepare the red blood cell suspension as required:
o For a suspension at 3%, mix 30µL of washed red blood cells with 970µL of 0.85% saline solution.
o For a suspension at 5%, mix 50µL of washed red blood cells with 950µL of 0.85% saline solution.
7. Mix gently until a homogeneous suspension is obtained.
What is the performance of the Ebram Immunohematology products?
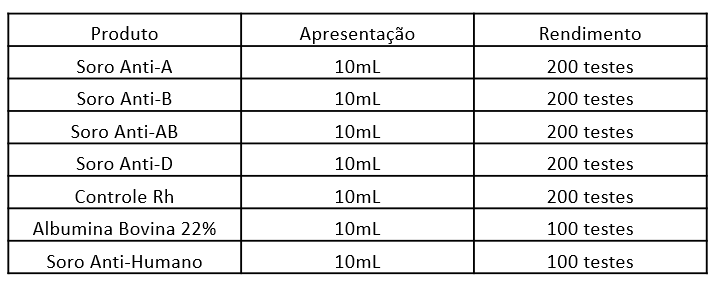
*The calculation was made considering the volume of 1 drop, equivalent to approximately 50 µL.
What is the function of Bovine Albumin 22%?
Bovine Albumin 22% plays an important role when added to the medium of antigen-antibody reactions. Its presence enhances this reaction, providing several fundamental advantages, such as:
- It facilitates the detection of IgG antibodies that are bound to red blood cells. In the absence of albumin, these antibodies would be more difficult to identify during the Antiglobulin phase.
- It helps to reduce the time needed for incubation. This optimizes the testing process, allowing for faster and more efficient results.
- It increases the sensitivity of the test, making it more capable of detecting antibodies, even at low concentrations, providing more accurate results.
Bovine Albumin 22% is recommended for the following tests: Pre-Transfusion Compatibility and Research and Titration of Blocking Antibodies.
What is the difference between monoclonal and polyclonal serums?
A monoclonal serum is produced from a single strain of antibody-producing cells. These antibodies are highly specific, recognizing and binding to a single antigen in a precise and targeted way. A polyclonal serum, on the other hand, is produced from multiple lineages of antibody-producing cells. This results in a mixture of antibodies with different specificities, capable of binding to different parts of the antigen.
Can Anti-Human Serum be used as a Coombs Serum? What is the difference between them?
Anti-human serum and Coombs' serum have the same indications for use, which is to carry out cross tests, research for irregular antibodies (Indirect Coombs') and Direct Coombs'. The difference lies in the composition of the reagents: anti-human serum is a combination of antibodies produced in immunized animals with specific human antibodies, including immunoglobulin (IgG) and the C3d fraction of complement. Coombs' serum, on the other hand, is monospecific, i.e. it is only specific for detecting IgG antibodies.
One of the advantages of anti-human serum is its ability to detect a wider variety of antibodies in red blood cells, because by combining the specificities for IgG and C3d we increase the sensitivity and specificity of the test. This is especially useful for identifying cases in which complement is activated, even when IgG levels may be low, reducing the risk of false negatives and providing additional information about the immune response.
Does the Ebram RH Control determine the RH factor?
No. Anti-D Serum is the serum used to detect the presence or absence of the D antigen, i.e. determination of the RH factor. The RH Control is a control test that should always be carried out in parallel with all the tests that use Anti-D Serum - Ebram, in order to detect false positive reactions caused by "rouleaux", cold agglutinins or autoantibodies.
Are there any Ebram products that require a license for controlled products from the federal police, civil police, army or Ibama?
No, there are no products in Ebram's range of reagents that require a license for controlled products.
Do the products in the Sorology range remain functional in the event of temperature variations during transportation?
Yes. Although transportation should preferably take place between 2-8 °C, the products in the Serology range maintain their functionality in the event of occasional temperature variations during transportation.
The reagents remain stable for up to 7 days at temperatures up to 37 °C.
Upon receipt, the products must be immediately stored under refrigeration at 2-8 °C to ensure their stability throughout use.
.
What precautions should be taken during the packaging and transportation of serology products?
Products should be stored and transported in an upright position to avoid leakage and the formation of particles in the latex reagent. With regard to the Les Latex product, it is crucial to avoid direct contact with ice or any condition that could cause the latex reagent to freeze, as this could result in the formation of particles in the product.
What are the sample restrictions for the Latex RF test?
The test must be carried out on serum samples. These samples can be stored for up to 24 hours at 2-8°C, or for up to 3 months at -20°C. Samples with strong lipemia, hemolysis or bacterial contamination should not be used. In addition, it is important not to use plasma samples, as fibrinogen can cause non-specific agglutination.
What is the difference between the Fr Waaler Rose and Fr Latex kit?
Both tests, Waaler Rose RF and Latex RF, are serological tests used to detect the presence of Rheumatoid Factor (RF), an autoantibody that is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. However, they differ in terms of methodology and clinical application.
- Waaler Rose RF: this test uses sheep red blood cells sensitized with rabbit IgG. When the patient's serum contains RF, a central halo is formed. It has greater clinical specificity, i.e. greater ability to correctly identify the presence of RF in patients with the disease, and is more commonly used in confirmatory cases.
- FR Latex: this is a direct agglutination test that uses latex particles coated with human IgG. When there is a reaction with the patient's serum, there is agglutination visible to the naked eye. It is a more sensitive, modern and simple method and is widely used in clinical screening.
Why are there two presentations of PCR Latex, ASO Latex and FR Latex?
Ebram sells two presentations of these products: the complete kit (latex reagent + positive control + negative control, spatulas and PVC plate) and just the latex reagent as an economical option. These two presentations allow customers to purchase the presentation that best suits their needs.
Why does Ebram's hCG test have a sensitivity of 25 mUI/mL and not 10 mUI/mL?
Because tests with a sensitivity of 10 mUI/mL are very sensitive, they can generate false positive results. They can detect very low levels of hCG that don't indicate a pregnancy or even cross-react with other hormonal substances, such as LH or TSH.
The sensitivity of 25 mUI/mL guarantees greater specificity, offering more reliable results for laboratory use.
What is the difference between the two presentations of Ebram's hCG test?
Ebram offers two presentations of the hCG test, both with a sensitivity of 25 mUI/mL. The difference lies in the presentation:
- Code 606: contains 50 individually wrapped strips. It is ideal for laboratories with lower demand and/or which prioritize greater security and control per unit.
- Code 607: contains 50 strips packed in a tube with silica gel. Suitable for laboratories with higher demand and/or those wishing to optimize their costs.
Both presentations maintain the same quality and performance, varying only according to the laboratory's needs.
Are the results of the immunochromatography pregnancy test reliable?
Immunochromatography pregnancy tests are reliable. However, as with any diagnostic test, there are certain factors that can interfere with the results, such as performing the test improperly and reading the results incorrectly. In addition, as it is a screening method, there may be some interfering factors that can cause a false result, such as: gestational and non-gestational trophoblastic diseases, low hCG concentration, ectopic pregnancy, drug use, pituitary gonadotropins such as LH and FSH, menopause, heterophile antibodies, anti-convulsant medication, anti-parkinsonism, hypnotics, tranquilizers and anti-acne medication.
I did the pregnancy test and a strong line appeared and another lighter line, is the result positive or negative?
The result is positive, after 5 minutes if there is only one colored line the test is negative, but if there are two lines, no matter how intense the color, the test is positive. A low concentration of hCG can result in a faint line in the region of the test line after a long period of time, so don't interpret the result after 5 minutes.
What are the most common errors that can occur when performing the hCG test?
Do not respect the limit line indicated on the pregnancy strip;
Do not respect the time specified in the instructions for use;
For code 607 - Inside the hCG tubes there is a silica gel to control humidity, so for the best performance of the hCG strips, the tube should remain closed after removing the strip for testing.
Is the procedure for carrying out the rapid tests the same regardless of the sample being used?
No. In order to carry out the tests correctly, it is necessary to read the instructions for use, as the volume of sample to be used and the need to use diluent may vary according to the type of sample to be tested.
What do the sensitivity and specificity values in rapid tests mean?
Sensitivity is the ability of a test to provide a positive result in patients who actually have the disease being investigated. Specificity is the ability of the same test to provide a negative result in non-diseased individuals.
What is the difference between the Dengue NS1 and Dengue IgG/IgM test?
NS1 is a marker of the acute phase of infection, even before the appearance of IgM and IgG class antibodies. It can already be found in the serum 24 hours after the onset of symptoms, and is also found in primary and secondary infections. IgM antibodies are found in around 80% of patients on the fifth day and around 99% of patients on the tenth day after contact with the virus and can persist in the circulation for up to three months and specific IgG antibodies become detectable days after the appearance of IgM. Their levels rise to a plateau and generally remain detectable for the rest of their lives.
Can the Vitamin D reagent be performed on any biochemical analyzer?
Ebram's Vitamin D reagent uses the immunoturbidimetry methodology and is compatible with automatic biochemical analyzers, without the need for specific equipment, thus offering practicality and flexibility for laboratories.
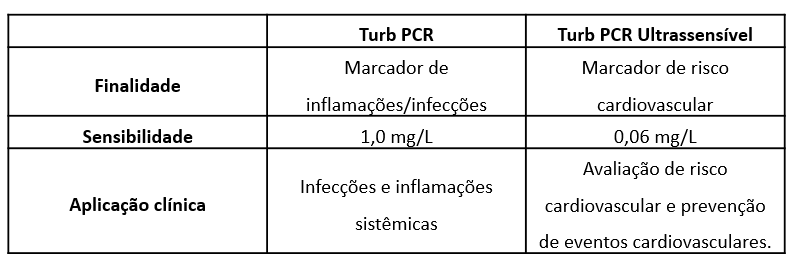
What is the difference between Ebram's Turb PCR and Ultrasensitive Turb PCR reagents?
Both reagents are used to measure C-reactive protein (CRP), but have different clinical purposes due to the difference in sensitivity.
Turb CRP is an inflammatory and infectious marker, used mainly to indicate and monitor infections and systemic inflammation. The Ultrasensitive Turb CRP is designed to detect very low levels of CRP and is indicated for assessing and monitoring cardiovascular risk, even in the absence of obvious inflammatory symptoms.
 Talk to a consultant (sales)
Talk to a consultant (sales)